what are the details of the us china trade deal ,Timeline of the US,what are the details of the us china trade deal,The United States and China have reached an historic and enforceable agreement on a Phase One trade deal that requires structural reforms and other changes to China’s economic and trade regime in the areas of intellectual property, technology transfer, agriculture, financial services, $189.00
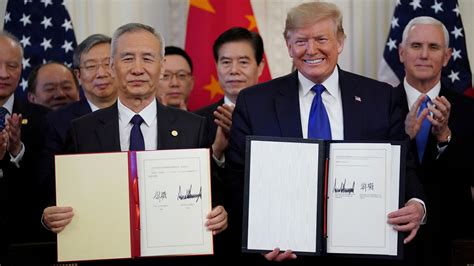
In January 2020, the United States and China entered into what was heralded as a landmark Phase 1 trade deal, aimed at easing the trade tensions that had plagued the two economic giants for over two years. The deal was signed during the administration of U.S. President Donald Trump, who had imposed tariffs on hundreds of billions of dollars' worth of Chinese goods, hoping to reduce the U.S. trade deficit with China and address concerns over intellectual property theft, forced technology transfers, and other unfair trade practices.
Fast forward to 2023, and the U.S. government under President Joe Biden has initiated a review of China's performance under the deal. The review, which includes an assessment of China’s compliance with the terms of the agreement, has become a focal point in the ongoing economic relations between the two superpowers. This article delves into the specifics of the U.S.-China Phase 1 trade deal, the key components of the agreement, its timeline, and the broader implications for global trade.
The U.S.-China Trade Deal: What’s In It?
The Phase 1 trade agreement between the U.S. and China was a significant step toward easing the trade conflict that had escalated since 2018. While the deal did not address every aspect of the trade dispute, it marked an important moment of compromise. The agreement consists of several key components, which fall under various categories including tariffs, intellectual property, technology transfers, and market access for American products in China.
# 1. Tariffs and Trade Balances
One of the most significant aspects of the Phase 1 deal was the commitment to a reduction in tariffs on Chinese goods. Prior to the agreement, the U.S. had levied tariffs on over $360 billion worth of Chinese imports. In response, China had placed tariffs on $120 billion worth of American products.
Under the Phase 1 deal, China agreed to increase its purchases of U.S. goods, particularly agricultural products, by at least $200 billion over two years. In exchange, the U.S. agreed to reduce some tariffs that had been imposed during the trade war, but many of the existing tariffs remained in place.
For instance, the U.S. agreed to halve the 15% tariffs imposed on $120 billion of Chinese goods in December 2019. However, tariffs on a further $250 billion worth of Chinese imports, which had been imposed earlier, remained untouched. This meant that while there was a reduction in tariffs, the trade imbalance was not entirely addressed in the Phase 1 agreement.
# 2. Intellectual Property (IP) Protection
A major concern for the U.S. throughout the trade war was the theft of intellectual property by Chinese entities. Under the Phase 1 deal, China committed to making significant changes to its intellectual property laws and practices to prevent the forced transfer of technology from American firms to Chinese companies.
China also agreed to enforce tougher penalties for IP violations, making it more difficult for companies to infringe on U.S. patents, copyrights, and trademarks. The Chinese government also pledged to improve its regulatory environment to ensure that foreign companies’ intellectual property was better protected.
# 3. Technology Transfers and Market Access
One of the sticking points in U.S.-China trade relations has been the forced technology transfers that American companies were subjected to in order to gain access to the Chinese market. In many cases, U.S. firms had to share proprietary technology with Chinese firms in exchange for market entry, which many considered an unfair practice.
The Phase 1 deal required China to implement changes to its policies regarding forced technology transfers. Specifically, China agreed to stop requiring foreign companies to transfer technology to Chinese firms as a condition of doing business in China. While this was a significant victory for the U.S., there were concerns about how effectively these commitments would be enforced.
Additionally, the deal included provisions for expanding market access for U.S. financial services and agricultural products in China. For example, China agreed to provide more favorable treatment to U.S. financial institutions, allowing them to operate more freely in the Chinese market. It also committed to increasing its purchases of U.S. agricultural products, including soybeans, pork, and corn, as part of the broader trade balance commitment.
# 4. Currency and Exchange Rate Policies
Another element of the Phase 1 trade deal was the issue of currency manipulation. The U.S. had long accused China of artificially devaluing its currency, the yuan, to gain an unfair trade advantage by making Chinese exports cheaper on the global market.
what are the details of the us china trade deal What are the popular Gucci replica belt designs available? Gucci belts come in a variety of designs and here are some of the popular designs i came across on DHgate and .To know if your Gucci belt is real or fake, check the “GUCCI” text engraved inside the belt. Fakes always have misplaced and thick inscriptions. See more
what are the details of the us china trade deal - Timeline of the US